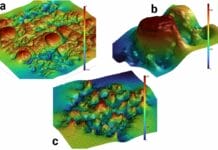
A study has found that a high-fat diet can have lasting implications on a person’s oral health. The research findings were presented in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology under the title, “Untargeted and Targeted Gingival Metabolome in Rodents Reveal Metabolic Links Between High-Fat Diet-induced Obesity and Periodontitis.”
Information About High Fat Diets
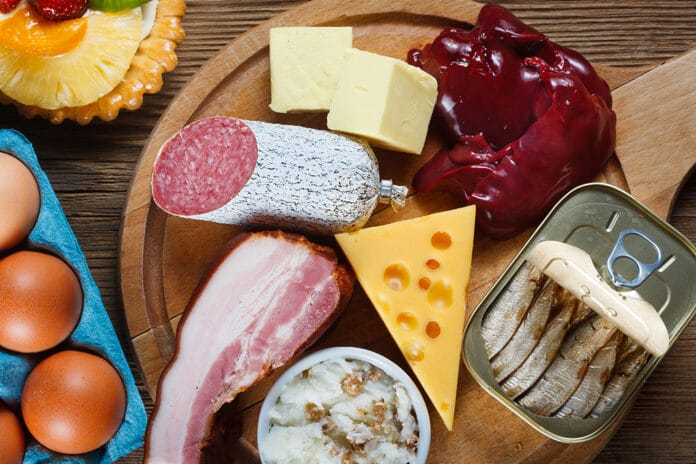
Your diet can have a lasting impact on your overall quality of life. A high-fat diet involves meeting most of your daily caloric needs with fatty foods. The diet usually focuses on eating foods with healthy, unsaturated fat like avocados and seeds and avoiding foods that are high in carbohydrates. People who prefer a high-fat diet may feel satiated for a longer period of time and experience more sustainable energy throughout the day.
Millions of people follow a high-fat diet because they want to improve their health and shed inches from their waistline. In fact, some of the most popular diet fads of the moment, such as the Atkins and Ketogenic diet, are considered high-fat.
Some common examples of high-fat foods include:
- Avocado
- Tofu
- Chia seeds
- Whole eggs
- Whole fat milk
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Coconuts
- Nuts
- Edamame
- Cheese
- Fatty fish
- Yogurt
- Dark chocolate
- Sunflower seeds
Our body powers itself with both fats and carbohydrates. Foods rich in carbohydrates can create glucose fuel, and the body can also use dietary fats to create energy. Many people enjoy high-fat diets because they can aid with weight loss, especially if the person consumes less sugar and carbohydrates.
About the Research Study
The purpose of this study was to examine how a high-fat diet can affect the obesity level in mice both with and without periodontitis. To do this, the team of researchers looked at the rodent’s gingival metabolome or the group of low molecular weight metabolites produced by cells during the process of metabolism. The metabolome can provide insight into the cellular activity and physiological status of the organism.
The research for this study was funded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Health Committee of Guangdong Province. Queensland University and Guangzhou Medical University also contributed grant money.
The Chinese scientists fed a group of 21 mice a high-fat diet over a 16-week period. To establish a control group, they fed another 21 mice foods that were low in fat. They also managed to induce the animal’s periodontitis on the left side using molar ligation for a span of 10 days. Meanwhile, the right side of the mouth was used as a control group. A combination of both targeted and non-targeted liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analyzed the gingival metabolome and arginine metabolism.
Based on their findings, the team of scientists discovered that the mice with periodontitis that were fed a high-fat diet revealed a much greater impact on their metabolism and periodontal disease than the control group. The results revealed that both periodontitis and a high-fat diet had distinct effects on the animal’s gingival metabolome.
Mice with periodontitis that had a low-fat diet scored 165, while the mice with periodontitis who ate a high-fat diet scored 885. The food from the high-fat diet also only altered 525 in the mice with healthy gingiva versus 1435 in mice who had periodontitis. Another piece of evidence that supported their claim was the K-medoids clustering, which demonstrated that a high-fat diet could strongly amplify the spread of periodontitis on the gingival metabolome.
In Conclusion
The Chinese research team believes a high-fat diet can greatly impact the oral health of obese patients. They support the scientific community to conduct more experiments to further examine the link between a high-fat diet and an amplified metabolic response that can worsen their periodontitis.
Before you leave, check out the Today’s RDH self-study CE courses. All courses are peer-reviewed and non-sponsored to focus solely on pure education. Click here now.
Listen to the Today’s RDH Dental Hygiene Podcast Below: